MDMA (3, 4 – methylenedioxymethamphetamine), also known as ‘ecstasy’ or ‘molly’, is a powerful synthetic drug that has hallucinogenic and stimulant properties.
Ecstasy has a half-life of 8 hours, by which time half of the drug will be clear of your system. After 40 hours, around 95% of the drug will be clear of your system.
Many factors, such as the dosage and personal profile of the person taking the MDMA, can influence how long it takes for your body to metabolise ecstasy.
How long does MDMA stay detectable in your system?
MDMA may still be detectable in your system for up to 90 days after you've taken the drug, depending on the method of drug testing being used.
After your last use, MDMA may remain in your system for weeks. Drug tests will be able to detect it in your blood and salvia for 1 or 2 days (24-48 hours), urine for up to 4 days (72 hours), and hair follicles for up to 90 days.
These can differ depending on factors like how much you've taken and how often you taken the drug.
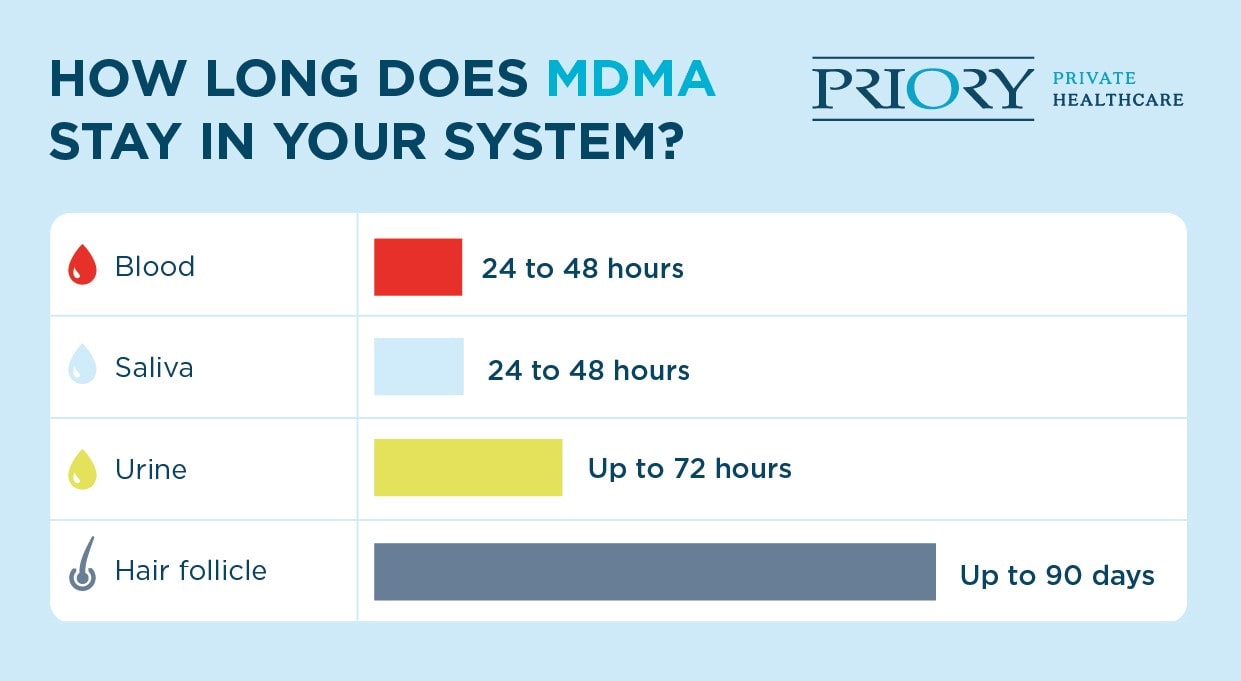
Different drug tests have different detection windows for MDMA:
Blood
A blood test can usually detect ecstasy in your system for around 1 to 2 days after it’s been consumed. However, in some cases, it can be detected in your blood for a longer period of time.
After ingesting, MDMA is quickly absorbed into your bloodstream, so can be detected within a couple of hours after use.
Saliva
Saliva tests can detect MDMA for 1 to 2 days after you last took it. As ecstasy is typically ingested via the mouth, it will be detectable immediately in your saliva after taking it.
Urine
MDMA can be detected in urine tests for up to 3 days after you’ve taken it. Depending on the dose, it could be detected in your urine in as little as 30 minutes after use.
Hair
Traces of ecstasy can be detected in your hair and hair follicles for up to 3 months after ingestion. This is due to small amounts of the drug entering blood vessels which then feed your hair follicles.
How does my body metabolise MDMA?
After ingestion, MDMA will eventually make its way to your liver, where most of it will be broken down. Here, it will be metabolised into chemical compounds called metabolites.
MDMA has a half-life (the amount of time it takes a drug's active substance to reduce from peak influence to half) of about 8 hours. After this time, around half of the drug will be passed through your system. It takes around 40 hours for 95% to leave your system.
After it's metabolised, your body will dispose of ecstasy in your urine or stool. This process could take longer depending on factors like the dosage, frequency of use and your body type.
Can I metabolise MDMA faster?
There is nothing you can do to accelerate your body's processing of MDMA. Once it is in your system, your liver will metabolise and dispose of it.
You may be tempted to drink lots of water, or exercise, to try and flush the drug out of your system. However, there is no evidence to suggest these will lead to MDMA leaving your system faster.
What factors affect how long MDMA stays in your system?
Different factors can affect how long MDMA stays in your system.
Dose and frequency of use
Higher doses of MDMA will take longer to be eliminated from your system than smaller doses. Additionally, frequent use of ecstasy typically results in the drug staying in your system longer compared to someone who uses it occasionally.
Method of consumption
The way MDMA is consumed can impact how long it stays in your system. The quicker the drug enters your bloodstream, the faster it will be metabolised and leave the body. Snorting MDMA allows it to reach the bloodstream faster than taking it orally, meaning it will be eliminated more quickly when snorted compared to being ingested as a tablet.
Body type
Some drugs and their by-products are stored in fatty tissues. Therefore, individuals with a higher body mass index (BMI) or more body fat may take longer to fully eliminate MDMA from their system.
Metabolism
People with faster metabolisms are able to process and remove drugs from their system quicker than those with slower metabolisms. Factors such as activity level, health conditions, and age can all influence metabolism. Generally, younger, healthier, and more active individuals can clear MDMA from their system faster than older individuals.
General health
Underlying health conditions may also affect how efficiently your body processes and eliminates MDMA. For example, if your liver or kidneys are not functioning properly, the drug may remain in your system for a longer period, as these organs are responsible for filtering and removing substances from your body.
Whether MDMA is mixed with other drugs
If you take ecstasy in combination with other substances, whether knowingly or unknowingly, this can slow down the elimination process as your body must process multiple substances simultaneously.







